Node.js is a runtime environment. It was built to enable JavaScript code to run outside the web browser since JavaScript was initially built to run on web browsers.
Node.Js runs on the V8 engine which is the fastest followed by the Chakra engine (used by Microsoft Edge)
In this article, we will look at Node.js Key features, Use-cases, how to setup Node.js locally, as well as best practices
I will also share links to useful resources to help you learn Node.js
Key features of Node.js
Some of the key features of Node.js include:
Asynchronous nature - this means it can handle multiple connections simultaneously. For instance, in situations where we have 2 events, events A and B, event B can take place without necessarily waiting for A to complete. This brings about the non-blocking I/O model
NPM(Node Package Manager) - NPM allows for easy dependency management. Node.js uses NPM. Through NPM we can get access to tons of libraries and tools for different roles such as Nodemon (a tool used to restart servers), ESLint (for code linting) and many more This also allows for code reusability => efficiency => time-saving

Single-Threaded - A task can be executed from the beginning to the end without interruption. This means only one statement can be executed at a time. Whenever there is a task, it is assigned a thread and other pending tasks will have to wait until the thread is assigned to them for execution to occur
It also uses the event loop, you can read more about event loop here
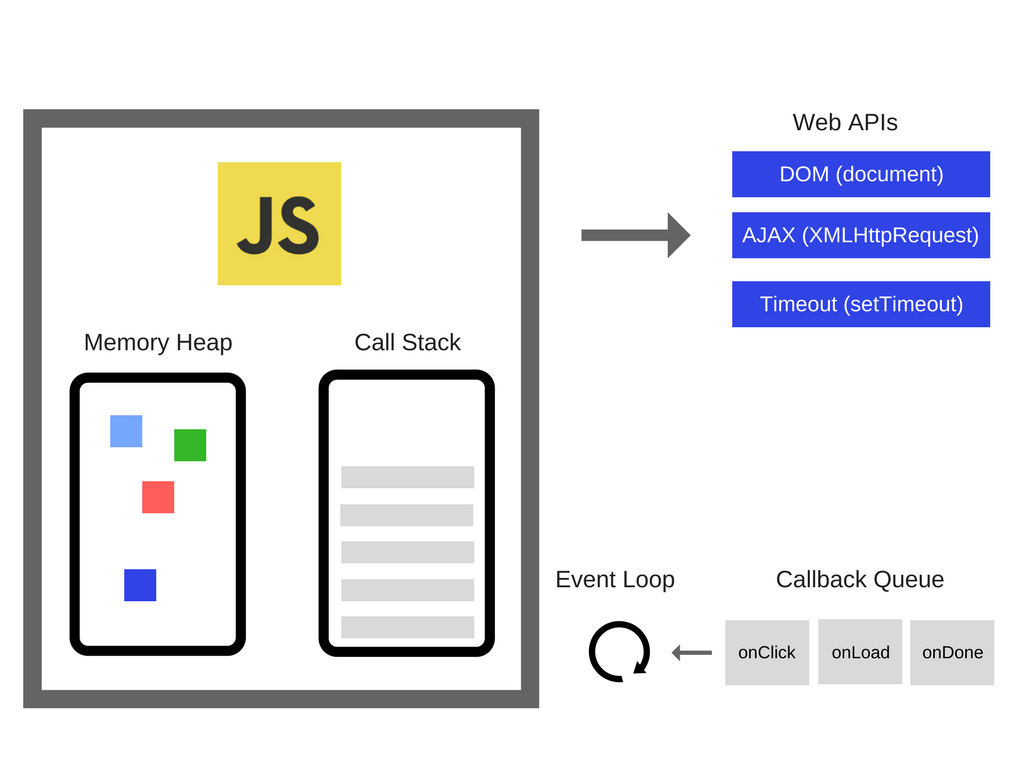
JavaScript everywhere - This means everything in Node.js is JavaScript code This means we can use our Js for the client side and also for the backend.
Use Cases of Node.js
Node.Js is used in:
Web applications - mostly to provide server-side functionalities
API servers - Node.js is used to create lightweight and efficient API servers
Real-time applications - it is suitable for building online games, chat apps and also collaborative tools
IoT(Internet of Things) - to handle data streaming, realtime analytics and device communication
Getting started
For this you need to install Node on Windows, Linux or MacOs
Create a new folder, inside it open a terminal window and type
npm init -yrun
npm installcommandcreate a file
server.jsand inside it, write the following snippetconst http = require('node:http'); const hostname = '127.0.0.1'; //refers to localhost const port = 3000; const server = http.createServer((req, res) => { res.statusCode = 200;// set status code to 200 (success) res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain'); res.end('Hello World\n'); }); server.listen(port, hostname, () => { console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`); }); // Server running at http://127.0.0.1:3000/On the terminal, type
node server.jsBoom, you are now running Node.js 🥳🥳🥳
In most cases, we use Express.Js inside Node.js (Fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for Node.js)
Express + Node.js guide
To get started,
Inside your working directory, open terminal window and run
npm init -yOn the terminal, run
npm install expressOreate
app.jsand inside it pasteconst express = require('express') const app = express() const port = 3000 app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Hello World!') }) app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`) })On the terminal, run
node app.jsBoom, now you are running Express.Js inside of Node.js
Challenges and Best Practices:
In most situations you are going to face some obstacles when using Node.js
Security - Node.js is vulnerable to (XSS) Cross-site scripting and SQL attacks. Best practice: Ensure Input validation, authentication and authorization mechanisms For instance, when dealing with user passwords, you can use a npm package; Bcrypt to handle encryption and decryption of passwords to and fro the database.

Error handling - use try/catch blocks and error middleware to manage errors effectively such as instances when the user enters wrong passwords, email etc.
Callback hell - deeply nested callbacks can make the code difficult to read and maintain.
Best practice: Use asynchronous patterns such as Promises, async/await to write a more readable code.
Performance monitoring - Use profiling tools to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance of Node.js applications.
Future trends of Node.js
Node.js is expected to play a major role in
Machine learning and AI - Developers will be using Node.js to build server-side APIs which handle real-time data processing
Serverless computing - Node.js is well-suited for serverless computing due to its lightweight and event-driven architecture
Edge computing - Node.js is likely going to be used for building apps that run on edge devices, resulting in efficiency
Case studies
Major applications, PayPal, Netflix, LinkedIn are all built with Node.js
One thing to note is that, they rarely slow down or crash. That is the beauty of building applications with Node.js
Resources to learn Node.js
Backend development and APIs with Node - https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn/back-end-development-and-apis/
Node.js Tutorial (codevolution Youtube) - https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLC3y8-rFHvwh8shCMHFA5kWxD9PaPwxaY
Introduction to Node.js (Official documentation) - https://nodejs.org/en/learn/getting-started/introduction-to-nodejs
Node and Express.js Full Course (Youtube) - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Oe421EPjeBE
It is important to note that while using these resources, focus on building projects rather than reading or watching passively